Where Are Diamonds Found?

Diamonds, the dazzling gemstones known for their brilliance and rarity, have a long and storied history as symbols of wealth, luxury, and enduring love. Mined from the depths of the Earth, diamonds are found in various corners of the globe, with certain countries standing out as major players in the diamond mining industry. In this article, we will delve into the geographical locations where the diamonds are found, exploring the top diamond-producing countries, along with key statistics and significant milestones in the diamond mining timeline. So, here is the answer to your “Where Are Diamonds Found”.
Top Countries In Diamond Mining
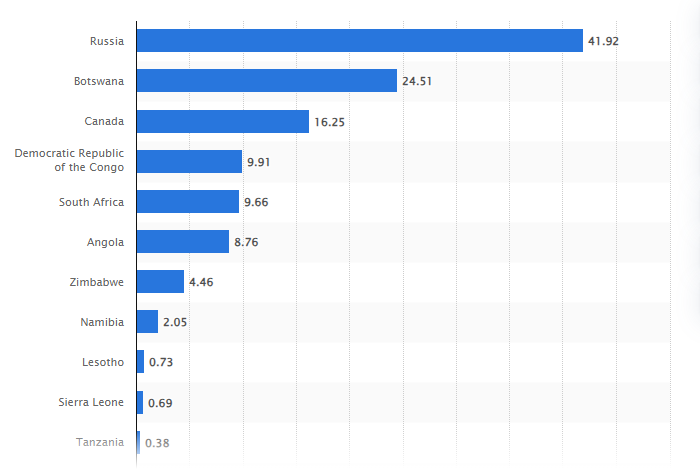
Diamond mining is a global industry, with several countries playing pivotal roles in the extraction and production of these precious gemstones. Leading the chart by Statista, Russia stands as a diamond mining powerhouse, contributing significantly to the world’s diamond supply. These top countries collectively contribute to the intricate web of the diamond mining industry, each playing a crucial role in shaping the world’s access to these exquisite gems.
Find The Best Diamond For You
1. Botswana – A Gem-Rich Haven
One of the leading countries in the diamond mining industry is Botswana, located in Southern Africa. For those curious about where can you find diamonds, Botswana has emerged as a major player in diamond production, thanks to its commitment to responsible and sustainable mining practices. The Jwaneng mine, often referred to as the “Prince of Mines,” is the richest diamond mine in the world and is a significant contributor to Botswana’s position as one of the top diamond-producing nations.
While Botswana is a very small country compared to other leading diamond-producing countries, it is the second-leading diamond producer in the world. Diamonds mined from Botswana have been incorporated into numerous royal jewelry including Meghan Markle’s engagement ring.
The discovery of diamonds in Botswana dates back to the 1960s, and since then, the country has steadily increased its diamond output. Statistics reveal that Botswana consistently produces millions of carats annually, contributing significantly to the global diamond supply.
2. Russia – A Diamond Powerhouse
Russia, the largest country on the planet, is also a major force in the diamond mining industry. For those wondering where are diamonds located in Russia, the answer lies in the rich diamond deposits found in Siberia, particularly the Yakutia region, is home to some of the world’s most productive diamond mines. The Mir mine, located in Yakutia, is famous for its enormous depth and vast diamond reserves.
According to statistics from 2022, Russia mines more than 41.92 million carats of high-quality diamonds in a single year which makes it one of the leading diamond producers of the world. Also, Russia is home to 14 alluvial placers that are counted among the trap sites located in rivers.
Russia’s involvement in the diamond trade dates back to the mid-20th century, and the country has maintained its status as a top producer over the years. The combination of harsh climates and challenging mining conditions has not deterred Russia from being a key player in the global diamond market.
3. Canada – A Newcomer With Impact
While Canada might not have the historical association with diamonds as some other nations, it has rapidly become a significant player in the industry. The question of where can I find diamonds often leads to Canada, especially the Northwest Territories, which has proven to be a treasure trove of diamond-rich deposits. Notable mines such as the Diavik and Ekati mines have contributed to Canada’s rising prominence in the global diamond market.
Canada is also known for many stunning diamonds including the 552-carat yellow diamond which is the largest incredible diamond that has ever been mined in North America.
Canada’s diamond production began in the 1990s, and since then, it has consistently increased its output. The Canadian diamond industry prides itself on ethical and environmentally responsible practices, appealing to consumers prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing.
4. South Africa – The Birthplace Of Diamonds
When exploring the question of where are diamonds located with a historical perspective, South Africa holds a special place in the history of diamonds as the birthplace of the diamond rush that began in the late 19th century. The discovery of diamonds in Kimberley and the subsequent rush transformed the region into a hub for diamond mining.
The world’s largest diamond, known as The Cullinan, was found in a South African mine. Discovered in 1905 at the Premier Mine in Transvaal, South Africa, this nearly flawless diamond weighed 3106 carats. Subsequently, it was meticulously cut into 9 significant diamonds, 96 smaller diamonds, and approximately 20 carats of unpolished chips.
South Africa’s diamond industry has faced many challenges, including the depletion of easily accessible diamond deposits. Even after so many challenges, the country still contributes significantly to global diamond production. There are notable mines, such as the Premier Mine and Cullinan Mine in South Africa. These mines have been instrumental in shaping South Africa’s role in the diamond market.
5. Australia – A Southern Hemisphere Contributor
Australia, known for its rich natural resources, is also a notable contributor to the global diamond supply. When considering where can I find diamonds of extraordinary colors, the Argyle mine in Western Australia was a significant answer, that gained fame for its production of pink diamonds, which is among the rarest and most sought-after in the world.
Diamond mining in Australia gained momentum in the 1980s with the establishment of major mines like Argyle. However, the Argyle mine ceased operations in 2020, impacting the global diamond market. Despite this closure, Australia remains a key player in the diamond industry, with the potential for new discoveries and projects in the future.
6. Democratic Republic Of The Congo (DRC) – Challenges And Opportunities
When considering where are diamonds located in Central Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, located in Central Africa, is home to extensive diamond deposits. However, the diamond trade in the DRC has been marred by issues such as conflict diamonds or “blood diamonds,” that are mined under conditions that involve human rights abuses.
Efforts have been made to address these challenges, including initiatives such as the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme, which aims to prevent the trade of conflict diamonds. Despite these challenges, the DRC continues to be a significant contributor to the global diamond market.
Also, till now DRC has been confined to a very specific and limited region. However, expanding the region holds a promise to increase the overall diamond production into multiples.
7. Zimbabwe – A Jewel In Southern Africa
Zimbabwe, situated in Southern Africa, has emerged as a notable player in the global diamond market. The Marange diamond fields, that was discovered in the early 2000s, have significantly contributed to Zimbabwe’s diamond production. This region is recognized for its rich diamond deposits, making it a focal point for those inquiring where can you find diamonds in Southern Africa.
Zimbabwe’s potential in the diamond industry remains substantial despite scrutiny regarding the management of its diamond resources. The Marange fields continue to be a key area of interest for diamond exploration and extraction.
While Zimbabwe has faced scrutiny regarding the management of its diamond resources, the country.
8. Namibia – Diamonds In The Desert
Namibia, a country with a diverse and unique landscape, is also a significant player in the diamond industry. When exploring where can you find diamonds in this southern African nation, the Namibian diamond fields, located in the Namib Desert, have been a source of economic growth for the country.
Diamonds in Namibia are present in alluvial deposits, mines located offshore, and elevated beach deposits along the coast. Miners in the country have developed creative methods to extract diamonds from the offshore locations.
Namibia’s commitment to sustainable diamond mining is a key factor behind its success in the diamond mining landscape. At the same time, marine diamond mining operations of Namibia add another dimension to the country’s diamond production.
9. Sierra Leone – Rising From Adversity
Sierra Leone, a West African nation, has faced challenges associated with conflict diamonds in its recent history. However, concerted efforts, including participation in the Kimberley Process, have aimed to address these issues and foster responsible diamond mining practices.
Sierra Leone’s diamond industry is gradually recovering, and the country continues to make strides in ensuring ethical and sustainable diamond production. The Koidu diamond mine, a notable location where diamonds are found in Sierra Leone, is a significant contributor to Sierra Leone’s efforts to redefine its role in the global diamond market.
10. Angola – A Diamond Treasure In Southern Africa
Angola, located in Southern Africa, is another key player in the global diamond market. The country’s diamond industry has witnessed significant growth, with notable mines like Catoca contributing to its status as a major diamond producer.
It’s been more than 100 years since Angola has been producing diamonds. A big share of diamonds in Angola are mined in the Lunda Norte and Lunda Sul provinces, representing key locations where the diamonds are found in the country.
The discovery of large and high-quality diamond deposits in Angola has brought the country into the spotlight of the global diamond trade. Efforts are going on to ensure responsible and sustainable diamond mining practices in Angola. It will further help Angola to enhance its role in the diamond production industry.
Diamond Reserves In Different Countries
As we move from the above section, it is clear that there are a number of countries that play their part in meeting the diamond demands around the world. There are more than 30 countries where the diamonds are found. While some countries own more market share in the industry, other countries have little market share. Here is the diamond reserve of top diamond mining countries:-
| Country | Diamond Reserve (in Carats) |
| Russia | 42 million carats |
| Botswana | 24 million carats |
| Congo | 16 million carats |
| Australia | 12 million carats |
| Canada | 11 million carats |
| Zimbabwe | 10 million carats |
| Angola | 9 million carats |
| South Africa | 8 million carats |
| Namibia | 2 million carats |
| Sierra Leone | 609 thousand carats |
Years of Excellence in Diamond Manufacturing
Diamond Rates Per Carat In Different Countries
Different countries have different rates of diamonds. The price mainly differs on the basis of local demand, supply chain differences, currency exchange rates, local taxes and duties, and import/export regulations.
| Country | Rates Per Carat (In USD) |
| Namibia | US$805.00 per carat |
| Sierra Leone | US$302.00 per carat |
| Canada | US$180.00 per carat |
| Botswana | US$156.00 per carat |
| South Africa | US$145.00 per carat |
| Angola | US$136.00 per carat |
| Russia | US$ 82.00 per carat |
| Zimbabwe | US$51.00 per carat |
| Australia | US$32.00 per carat |
| Congo | US$8.00 per carat |
Surprisingly, Namibia and Sierra Leone yield the smallest annual diamond output; however, the diamonds they produce boast the highest global value. It’s essential to note that superior-quality, high-value diamonds typically find their way into the jewelry market, whereas lower-value diamonds are utilized in various industries. It’s a testament to their commitment to quality over quantity, showcasing that where was diamond found can impact its value significantly.
What Are Blood Diamonds?
Blood diamonds are also known as conflict diamonds. The term refers to diamonds that are mined in war zones and sold to finance an insurgency. The sale of these diamonds is used to fund armed groups and rebel movements, contributing to conflict, civil unrest, and human rights abuses in affected regions. The term “blood diamond” gained prominence in the late 1990s when the global community became increasingly aware of the connection between diamonds and violent conflicts.
Key characteristics and issues associated with blood diamonds include:
Conflict Financing
The primary issue with blood diamonds is their role in funding armed conflict. Rebel groups, insurgents, and warlords often exploit diamond mines to generate revenue for purchasing weapons, funding military operations, and sustaining their illegal activities.
Human Rights Abuses
The extraction and trade of blood diamonds are frequently associated with severe human rights violations. Miners and local communities in conflict zones may face exploitation, forced labor, violence, and displacement. The profits from these diamonds often contribute to the continuation of such abuses.
Environmental Degradation
Diamond mining in conflict zones may involve environmentally destructive practices, such as unregulated and unsustainable mining methods. The lack of oversight and adherence to environmental standards can lead to long-term damage to ecosystems and surrounding areas.
Illicit Trade Networks
Blood diamonds enter the global diamond market through complex and illicit channels, making it challenging to trace their origin. This lack of traceability allows these diamonds to mix with ethically sourced diamonds, posing a significant ethical challenge for the diamond industry.
Global Response
In response to the issue of blood diamonds, the international community established the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) in 2003. The Kimberley Process aims to prevent the trade of conflict diamonds by implementing a system of certification and monitoring. Participating countries commit to ensuring that diamonds are conflict-free, and non-compliant regions are banned from the legitimate diamond trade.
Conclusion
The question of where are diamonds found leads to diverse answers, from the vast diamond fields in Botswana to the marine diamond deposits off Namibia’s coast. Countries like Russia, with its extensive Siberian mines, and Canada, with its rich Northwest Territories, contribute to the global diamond supply, each region adding its unique chapter to the story of diamonds.
Diamonds originated from the Earth’s mantle and brought to the surface through geological processes, continue to captivate the world with their beauty and rarity. The global diamond mining landscape is dynamic, with various countries playing pivotal roles in shaping the industry. From established players like Botswana and Russia to newcomers like Canada, Zimbabwe, Namibia, and Sierra Leone, the story of diamonds is one of geological wonders, human enterprise, and the pursuit of ethical and sustainable practices.
As technology advances and discoveries are made, the landscape of diamond mining will inevitably evolve. The allure of diamonds, however, remains timeless, and understanding the geographical origins of these precious gems adds a layer of appreciation for each diamond’s journey from the depths of the Earth to adorning the most exquisite jewelry.
FAQ’s On Where Are Diamonds Found
1. Where is diamond found on earth?
Diamonds are found on Earth in various locations, typically in regions where the Earth’s mantle has brought them closer to the surface through volcanic activity or tectonic processes. Diamond mines are distributed globally, with significant deposits in countries like Botswana, Russia, Canada, Australia, South Africa, Namibia, and others, answering the question of where the diamonds are found
2. What rock is diamond found in?
Diamonds are often found in a type of rock called kimberlite. Kimberlite is a volcanic rock that originates from the Earth’s mantle and is known for carrying diamonds to the Earth’s surface. Lamproite and alluvial deposits are other types of rocks where diamonds can be found.
3. Is diamond found in nature?
Yes, diamonds are found in nature. They are natural minerals that form deep within the Earth’s mantle under high pressure and temperature conditions. Through geological processes, diamonds are brought closer to the Earth’s surface, where they can be mined.
4. Where diamonds can be found?
Diamonds can be found in various countries around the world. Major diamond-producing countries include Botswana, Russia, Canada, South Africa, Namibia, Australia, and others. Diamond mines are often located in kimberlite pipes or alluvial deposits, answering the question of where can you find diamonds globally.
5. Where was diamond first found?
The first recorded discovery of diamonds was in India, where they have been mined for centuries. The Golconda mines in India were particularly famous for producing some of the world’s most renowned diamonds, including the Koh-i-Noor and the Hope Diamond.
6. Which country has the best diamonds?
Determining the “best” diamonds is subjective and can depend on factors such as size, color, and clarity. However, countries renowned for producing high-quality diamonds include Botswana, Russia, Canada, South Africa, and Namibia, showcasing where the best diamonds can be found.
7. Where is the best place to find diamonds?
The best place to find diamonds depends on various factors. Historically, significant diamond deposits have been discovered in countries like Botswana, Russia, Canada, and South Africa. However, the availability of diamonds is also influenced by geological conditions and mining practices.